Dioxus Fullstack
Almost all apps need a remote server to store and update user data. Dioxus provides a number of fullstack utilities for building your app's server alongisde the client. With Dioxus Fullstack, you can build both your app's frontend and backend entirely in Rust!
Dioxus Fullstack deeply integrates with the popular Axum framework, making it easy to quickly add complex functionality to your app, including:
- Server-Side-Rendering: Render HTML on the server and hydrate it on the client
- Server Functions: Type-safe Axum HTTP endpoints directly callable from the client
- Hot-Reload: Rapid Rust hot-reload during development powered by subsecond
- Typed Routing: Easily extract queries and paths from the URL
- Multi-part Forms: Capture multipart form data from the client into typed Rust structs
- Binary Streams: Easily add file upload/download backend capability
- SSE and WebSockets: Complex, stateful datatypes for server communication
- Asset Management: Automatically optimizes assets for deployment to CDNs
- WASM Support: Deploy to WASM-based providers like Cloudflare Workers
- Bundle Splitting: Split apart large WASM blobs on a per-route basis
- Static Site Generation: Generate HTML markup perfect for blogs and static sites
Currently, Dioxus Fullstack does not provide built-in utilities for things like Databases, Caches, Sessions, and Mailers. Our current focus is to finish polishing the fullstack integration before branching out into a more "complete" fullstack solution. You'll need to pull in 3rd-party crates like Sqlx and tower-sessions to use such features. To help, we provide a few examples in the Dioxus GitHub repo to get started.
Hot-Reload
With Dioxus, our goal is to maximize your developer productivity. Dioxus Fullstack ships with full Rust hot-reload support built-in thanks to our hot-patch engine subsecond. Subsecond uses advanced assembly and linker techniques to allow modifying Rust functions at runtime. You can add new endpoints, pages, and logic to your app without manually rebuilding.
Subsecond currently has a few limitations. For the best experience, we recommend only modifying code in the "tip" of your app. Note that code that runs only once will not be hot-reloadable and will require a restart of the app.
Server functions
Dioxus Fullstack provides an easy way to communicate with the server from any client. Server functions let you define a function that always runs on the server. When you call that function from the client, Dioxus will automatically serialize the arguments, send them to the server, run the function on the server, serialize the return value, and send it back to the client.
// The body of the function will always run on the server so we can do server-side operations like database queries #[get("/api/dog/{breed}")] async fn fetch_dog(breed: String) -> Result<String> { DB.execute("SELECT url FROM dogs WHERE id = ?1", &breed) }
We can use the results of server functions during server-side-rendering along with hydration:
let url = use_loader(|| fetch_dog("poodle".to_string()))?; rsx! { img { src: "{url}", alt: "A cute dog" } }
Server functions are described in more detail in the server functions guide. In addition to this guide, you can find more examples of fullstack apps in the examples directory.
Websockets and Streams
Dioxus Fullstack comes with full support for Axum, and with it, special client handlers for things like WebSockets and HTTP Streams. We provide a number of utilities like use_websocket to reactively manage these resources on the client.
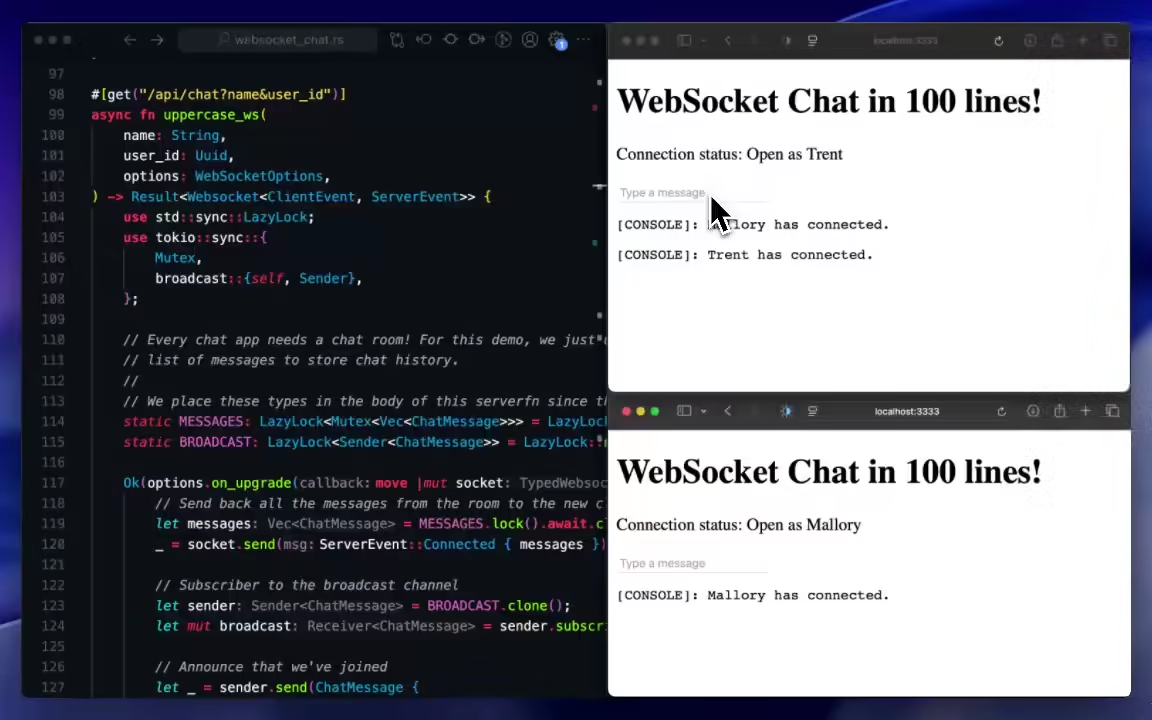
Our Streaming<T> wrapper allows you to easily send arbitrary bytes, text, JSON, and chunked file contents to and from the server. Easily roll your own hybrid client-server types by implementing IntoRequest and FromResponse!
Server Side Rendering
Dioxus Fullstack allows you to render your app on the server, speeding up load times for your users and improving your site's discoverability for search engines like Google. Server-side-rendering (SSR) allows you to render your app's initial HTML on the server, sending a fully-formed HTML document to the client. The client can then "hydrate" the HTML into a fully-interactive app that can continue running on the client without requiring a persistant server connection.
Assets
Because Dioxus Fullstack integrates with our build tool DX, your fullstack apps come pre-optimized for deploying onto infrastructure like content-distribution-networks (CDNs). CDNs reduce your bandwidth usage and speed up your app's time-to-first byte for maximum performance. Assets bundled with DX are hashed, letting the client infinitely cache their contents.